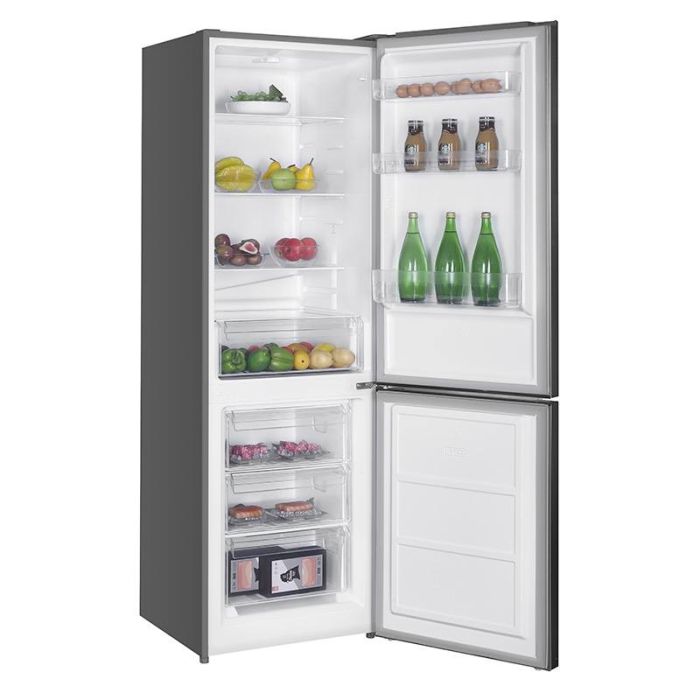
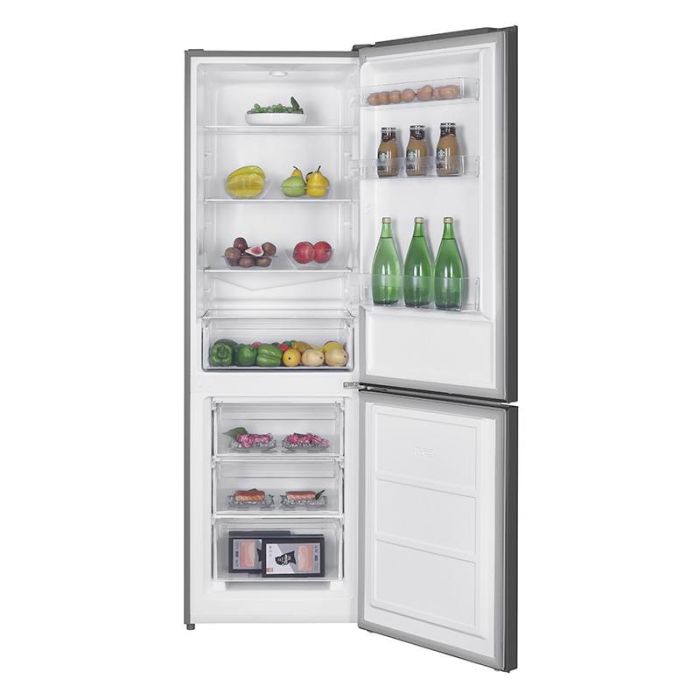
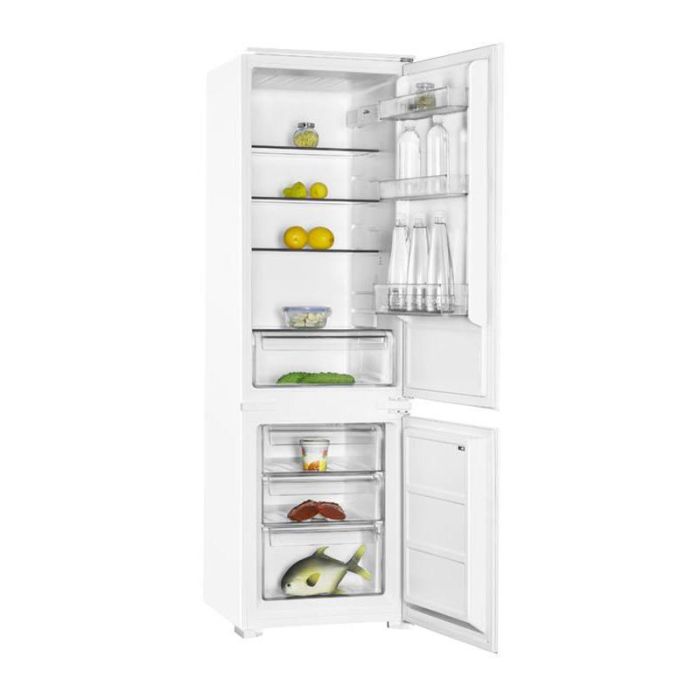
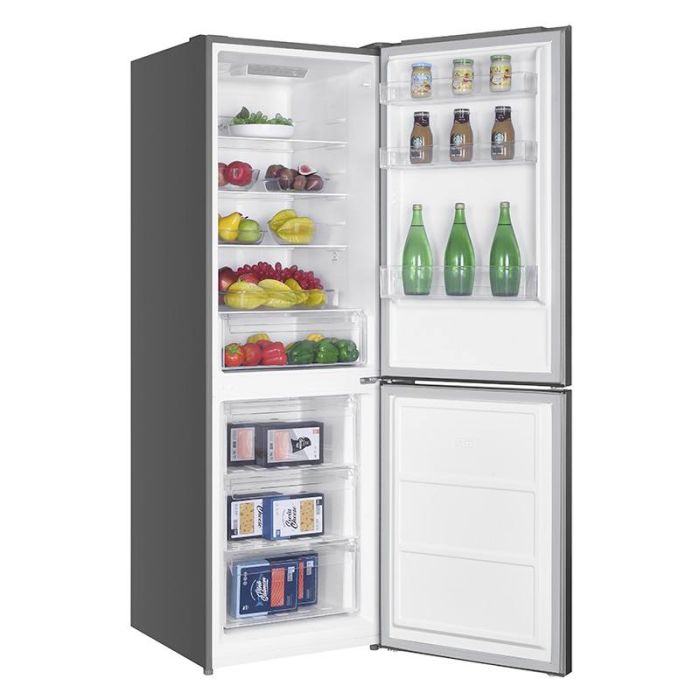
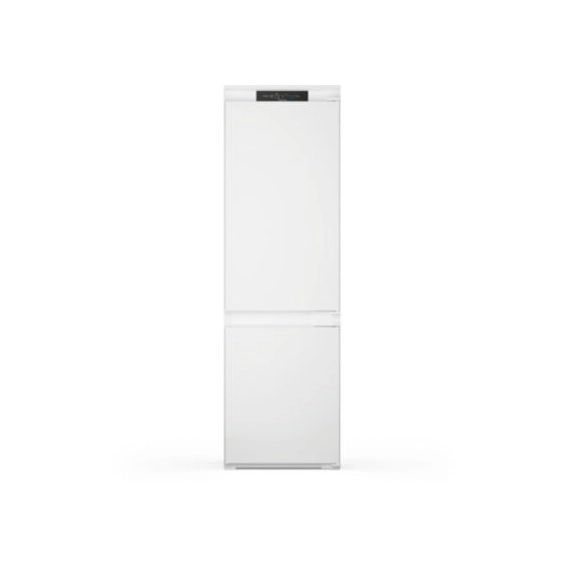
Frigo/réfrigérateur Valberg sous garantie Valberg à Paray-Vieille-Poste - Gros électroménager d'occasion

BOSCH KGV36VBEAS - Réfrigérateur combiné - 307 L (213 + 94 L) - Froid low frost - L 60 x H 186 cm - Noir - Achat / Vente réfrigérateur classique BOSCH KGV36VBEAS - Réfrigérateur combiné - 307 L (213 + 94 L) - Froid low frost - L 60 x H 186 cm - Noir ...
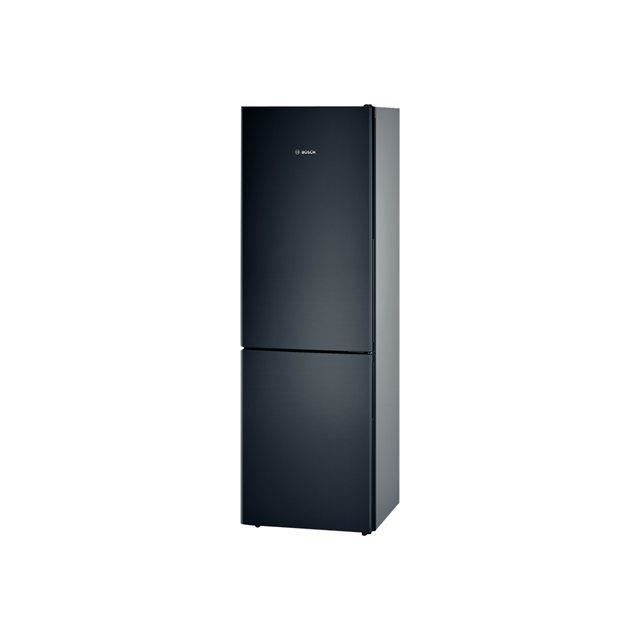

BOSCH KGV36VB32S - Réfrigérateur combiné - 307 L (213 + 94 L) - Froid low frost - A++ - L 60 x H 186 cm - Noir - Achat / Vente réfrigérateur

Réfrigérateurs congélateurs (combinés et 2 portes) - VALBERG CS 313 F WD X742C (CS313FWDX742C) | Nouveaux-Consos